Development of GOF/LOF variant database for clinical support applications and therapeutic target discovery in genetically intractable diseases and cancer
Abstract
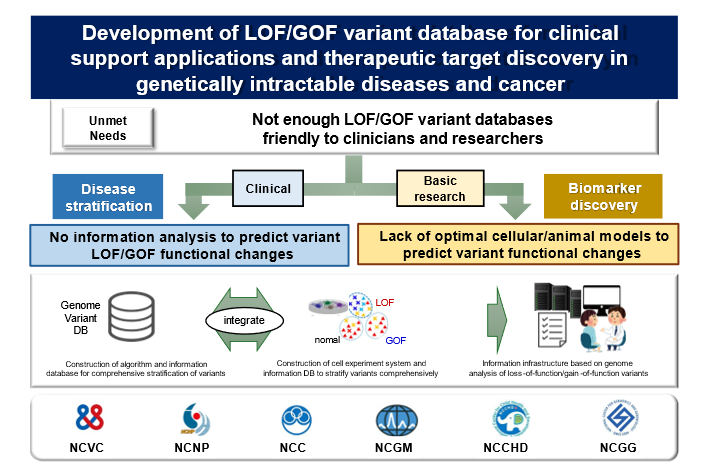
The development of genome analysis technology has been progressing, and genome information related to diseases has been accumulating. This information has been of great help in genetic diagnosis of intractable diseases, basic research to clarify molecular mechanisms, and development of new drugs to overcome diseases.
However, only a small fraction of the accumulated genome information has been registered as pathogenic variants that cause diseases, and many of them still remain as variants of unknown significance. Accumulation of new information and detailed analysis are necessary to make this information for future research.
Therefore, in this study, we will use two methods to study representative disease-causing genes; i) to develop an information analysis algorithm to analogize the degree of influence of gene variants on protein function changes, and ii) to construct a database to stratify variant functions based on information obtained from a comprehensive cellular function analysis system of gene variants.
We hope to conduct research that can overcome barriers in medical research and clinical practice by having the 6NCs work together to understand diseases by taking advantage of their respective characteristics.
Image
Perspectives
The results of this research will be shared widely among 6NCs' researchers to build a next-generation disease genome information platform that can be used for medical treatment and basic research.
The detailed evaluation of loss-of-function and gain-of-function variants obtained through this research and the stratification of case pathologies based on this evaluation will greatly contribute to the promotion of personalized medicine.
Comments from principal researcher
Yoshihiro Asano, MD. Ph.D.
Director, Department of Genomic Medicine / Biobank
National Cerebral and Cardiovascular Center

To achieve the goal of social implementation of genomic medicine, it is necessary to accumulate information that is easy to use for practicing physicians and researchers. This is an issue common to the disease areas of each National Center, and we will actively utilize the latest information analysis and research technologies to build a platform that can promote information sharing and collaborative research.
Shared Researchers
National Cancer Center Research Institute
Kouya Shiraishi
National Center for Global Health and Medicine
Noriko Miyake
National Center of Neurology and Psychiatry
Ichizo Nishino
National Center for Child Health and Development
Tomoko Kawai
National Center for Geriatrics and Gerontology
Kouichi Ozaki