Elucidating the marker of atrial-specific fibroblasts and their function
Abstract
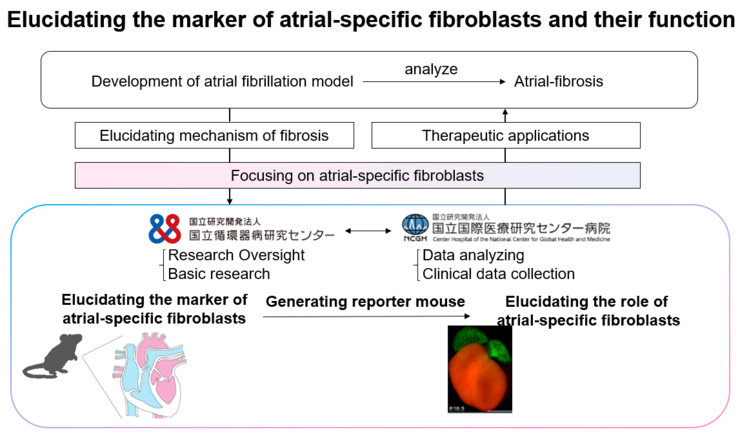
Atrial fibrillation is the most prevalent arrhythmia in Japan, and the development of a new treatment for atrial fibrillation is an urgent issue. Despite the clinical importance of this disease, there is no simple and stable mouse model to induce atrial fibrillation, and it has been difficult to investigate the pathogenesis of atrial fibrillation in detail in mice.
Therefore, we have been developing a mouse model of atrial fibrillation. At the same time, since fibrosis is involved in the pathogenesis of atrial fibrillation, we thought that elucidating the molecular mechanism of fibrosis in the atria may help prevent and treat atrial fibrillation. Fibroblasts are the cells that cause fibrosis, and the gene expression profile of fibroblasts in the ventricle has already been clarified. On the other hand, the function of atrial fibroblasts has not been elucidated, although there are scattered reports that their gene expression is different from that of fibroblasts localized in the ventricle. In this study, we will identify markers of atria-specific fibroblasts in mice and elucidate their function and role in atrial fibrillation. This will elucidate the profile of fibroblasts that cause atrial fibrosis, a previously unknown mechanism of atrial fibrillation, and will shed light on one aspect of the pathogenesis of atrial fibrillation at the molecular level, which is expected to be applied in future therapies for the eradication of atrial fibrillation.
Perspectives
If this study shows that atrial-specific fibroblasts play a role in the development of atrial fibrillation, it is expected that atrial fibrillation can be treated by eliminating these fibroblasts. Ultimately, in the absence of medical treatments for atrial fibrillation, it is hoped that a drug targeting atrial-specific fibroblasts will be created, and that this will lead to a cure for atrial fibrillation.
Comments from principal researcher
Naofumi Yoshida,National Cerebral and Cardiovascular Center Research Institute,
Research,Department of Advanced Medical Technologies,Laboratory Chief
As a cardiologist, I have treated many patients with atrial fibrillation. Atrial fibrillation can develop without the patient being aware of it and can lead to embolisms such as cerebral infarction. I hope that this study will advance the understanding of the pathophysiology of atrial fibrillation and provide knowledge that can be utilized in the prevention and treatment of atrial fibrillation in the future.

Shared Researchers
Yoshinari Enomoto,National Center for Global Health and Medicine,Department of Cardiology